Preventing Knee Joint Damage in the Elderly: A Guide to Healthy Aging
Knee joint damage is a common concern for the elderly, often leading to pain, reduced mobility, and a decreased quality of life. However, with the right preventive measures, many cases of knee joint damage can be avoided or delayed. This article outlines strategies to prevent knee joint damage in the elderly and provides an example of how these strategies can be implemented.
Understanding Knee Joint Damage
Knee joint damage, often referred to as knee osteoarthritis, is a degenerative condition where the cartilage in the knee joint wears down over time. This can be due to age, injury, obesity, or overuse. The resulting friction between bones can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness, significantly impacting mobility.
Strategies to Prevent Knee Joint Damage
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a leading risk factor for knee osteoarthritis. Reducing body weight can significantly decrease the load on the knees, thus reducing stress and wear on the joint.
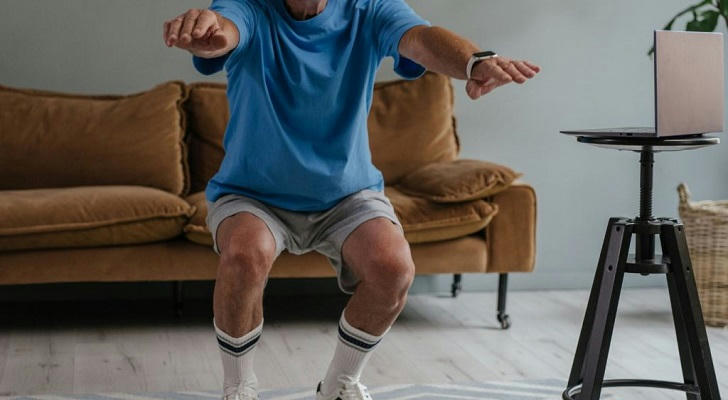
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular, low-impact physical activity can strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing better support and reducing the stress on the joint. Exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking are beneficial.
Strengthening and Flexibility Exercises
Specific exercises targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can improve knee stability. Flexibility exercises, like stretching, can also enhance the range of motion and reduce the risk of injury.
Proper Nutrition
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly calcium and vitamin D, can help maintain strong bones and joints. Foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fish are excellent sources.
Joint-Friendly Activities
Avoiding high-impact activities that put excessive stress on the knees, such as running or jumping, can help prevent damage. Opting for low-impact activities is a wise choice.

Footwear with Proper Support
Shoes with good arch support and shock absorption can reduce the stress on the knees. This is particularly important for those who are overweight or have flat feet.
Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups can help detect early signs of knee joint damage. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening.
Pain Management
Managing pain effectively can prevent overcompensation and further damage. Using ice, anti-inflammatory medications, or seeking physical therapy can help manage knee pain.
Example: Mrs. Johnson’s Prevention Plan
Let's consider the case of Mrs. Johnson, a 72-year-old retired teacher who wants to prevent knee joint damage.
Weight Management: Mrs. Johnson, who is slightly overweight, decides to adopt a healthier diet and starts walking daily to lose weight. She works with a nutritionist to create a meal plan that is low in fat and high in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
Exercise Routine: She incorporates swimming and cycling into her weekly routine, doing each three times a week. She also attends senior yoga classes to improve flexibility and balance.
Strength Training: Mrs. Johnson works with a physical therapist to create a strength training program focused on her leg muscles. She performs these exercises twice a week.
Nutrition: She ensures her diet includes adequate calcium and vitamin D, taking supplements when necessary, especially during the winter months when sunlight exposure is limited.
Appropriate Footwear: Mrs. Johnson invests in a pair of walking shoes with good arch support and shock absorption. She also uses knee sleeves when participating in more strenuous activities.
Regular Monitoring: She schedules regular check-ups with her doctor to monitor her knee health and to address any issues promptly.
By following these strategies, Mrs. Johnson is able to maintain her knee health, remain active, and enjoy her golden years without the的困扰 of knee joint damage.

Conclusion
Preventing knee joint damage in the elderly is achievable through a combination of healthy lifestyle choices and proactive healthcare. By maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, ensuring proper nutrition, and wearing appropriate footwear, seniors can significantly reduce their risk of knee osteoarthritis. It's never too late to start taking steps to protect your knees and enjoy an active, pain-free retirement.
